Molecular Biology and Biomedical Science Laboratory is where theoretical knowledge meets real-world application. It provides students with comprehensive hands-on training to master modern experimental techniques fundamental to life science research and clinical applications.
Beyond the BenchWe don't just teach techniques; we build careers. The laboratory curriculum integrates theoretical knowledge with practical experience in DNA and RNA extraction, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), gel electrophoresis, protein analysis, cell culture, microscopy, and biochemical assays. Through structured laboratory modules and collaborative projects, the laboratory develops students’ technical competence, critical thinking, and scientific communication skills, preparing graduates for advanced study, research, and careers in biomedical and biotechnology fields.
Microbiology labs are specialized facilities designed to study microorganisms—bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. These labs are equipped with various tools and technologies to facilitate research, diagnostics, and applications in fields like medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. Here’s an overview of the key facilities and equipment typically found in microbiology labs:

Purpose: Provide a sterile environment to handle pathogenic or sensitive microorganisms safely.

Purpose:Maintain optimal temperature conditions for the growth of microorganisms.

Purpose: Sterilize equipment and media using high-pressure steam.
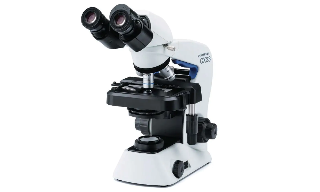
Purpose: Allow visualization of microorganisms at high magnification.

Purpose: Provide nutrients for the growth of microorganisms.

Purpose: Separate components of a sample based on density.

Purpose: Accurately measure and transfer small volumes of liquids.

Purpose: Mix samples rapidly by vortexing.

Purpose: Maintain samples at a constant temperature for various procedures.
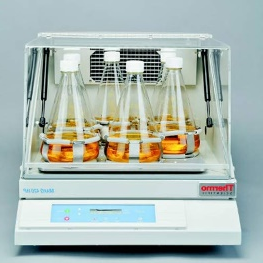
Purpose: Provide agitation for liquid cultures.
Genetics and protein labs focus on understanding the genetic basis of traits, gene expression, and protein functions. These labs require specialized equipment and facilities to conduct experiments involving DNA, RNA, proteins, and other biomolecules. Here’s a detailed overview of the typical facilities and equipment found in genetics and protein labs:
Genetics Labs Facilities
1. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Machines
o Purpose: Amplify specific DNA sequences.
2. Real-Time PCR Machines (qPCR)
o Purpose: Quantify DNA or RNA in real-time during amplification.
3. Gel Electrophoresis Systems
o Purpose: Separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on size and charge.
4. DNA Sequencers
o Purpose: Determine the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
5. Centrifuges
o Purpose: Separate DNA, RNA, or protein samples based on density.
6. Spectrophotometers
o Purpose: Measure nucleic acid and protein concentrations by analyzing light absorbance.
o Types: UV-Vis spectrophotometers.
Protein Labs Facilities
1. Protein Electrophoresis Systems
o Purpose: Separate proteins based on size (SDS-PAGE) or isoelectric point (IEF).
Cell biology labs are designed to study the structure, function, and behavior of cells. These labs often require specialized equipment and facilities to perform experiments related to cell culture, imaging, molecular biology, and biochemistry. Here's an overview of the key facilities and equipment typically found in cell biology labs:
Basic Facilities and Equipment
Cell Culture Hoods: Provide a sterile environment to handle and manipulate cell cultures. Includes laminar flow hoods and biosafety cabinets (Class II and III).
Incubators: Maintain optimal temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels for cell growth. Includes CO₂ incubators and shaking incubators.
Light Microscopes: Standard microscopes for visualizing cells and tissues. Includes brightfield, phase contrast, and differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopes.
Fluorescence Microscopes: For imaging fluorescently labeled cellular components.
Overall, cell biology labs are equipped with a variety of tools and technologies to facilitate research on cellular processes, cell interactions, and the effects of different treatments on cells. The specific setup may vary depending on the lab's research focus, whether it is studying cell signaling, cell development, cancer biology, or other aspects of cell biology.